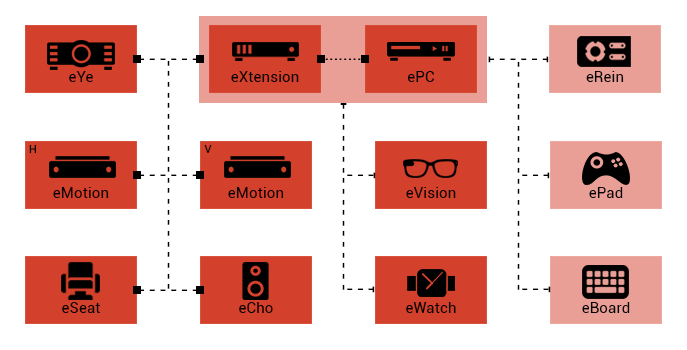
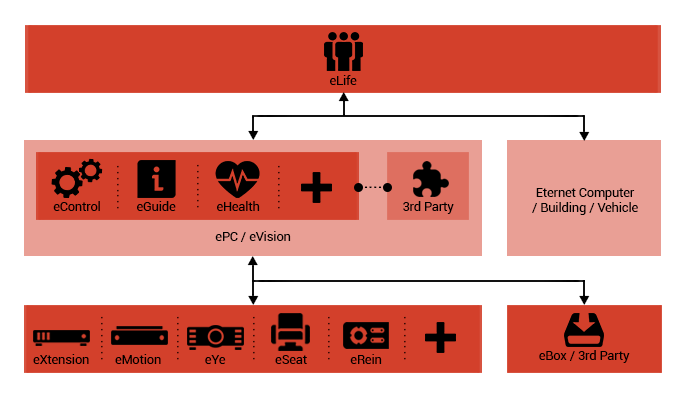
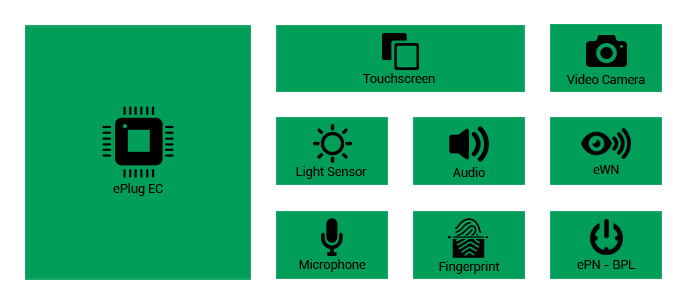
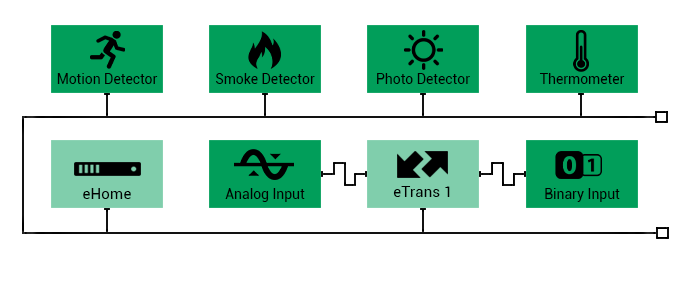
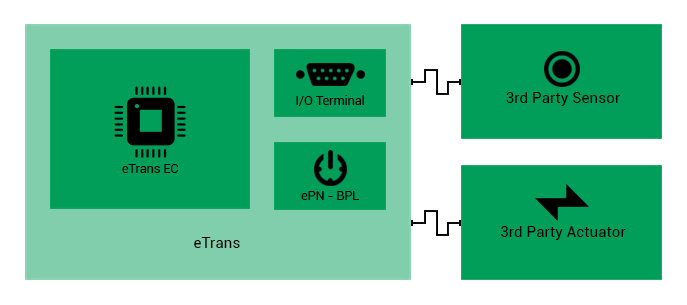
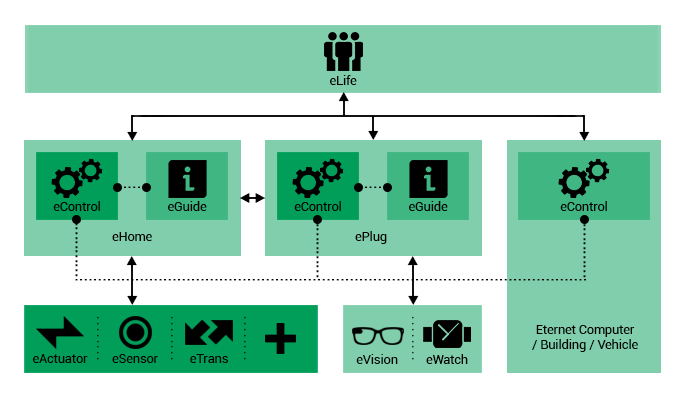
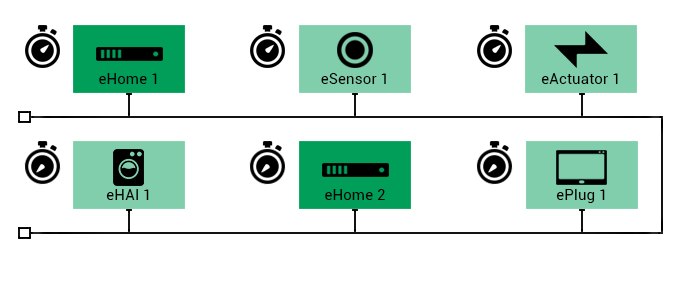
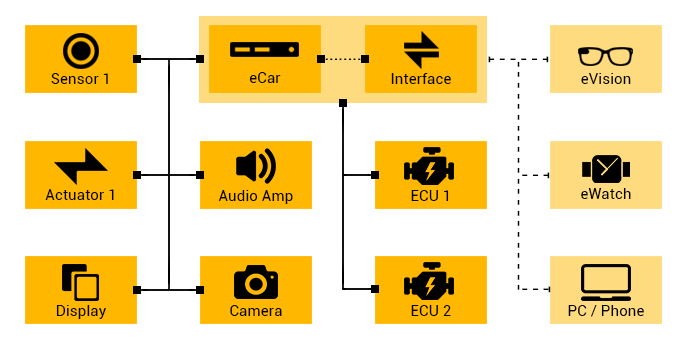
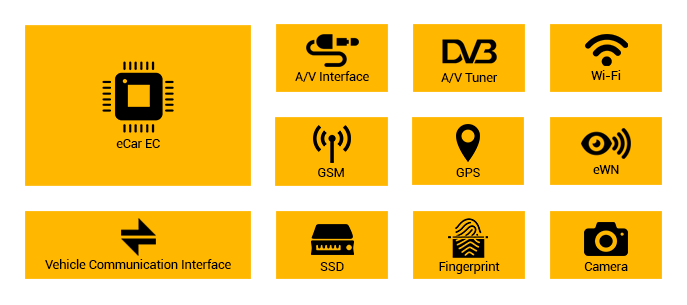
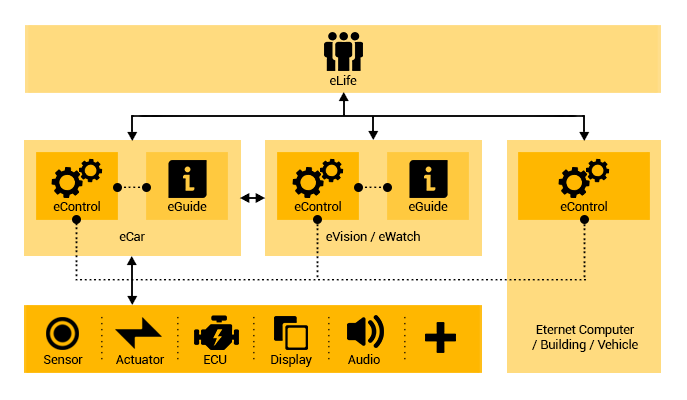
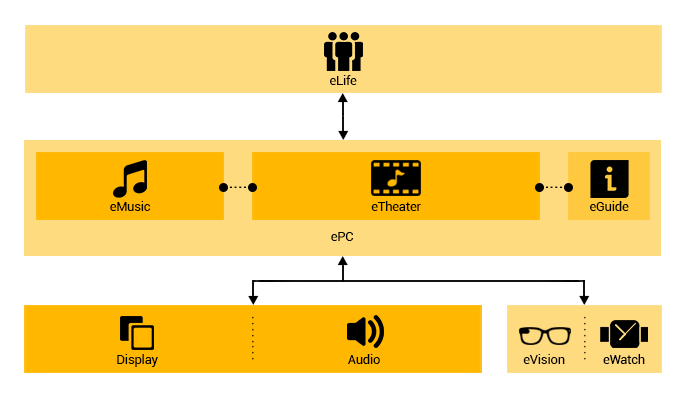
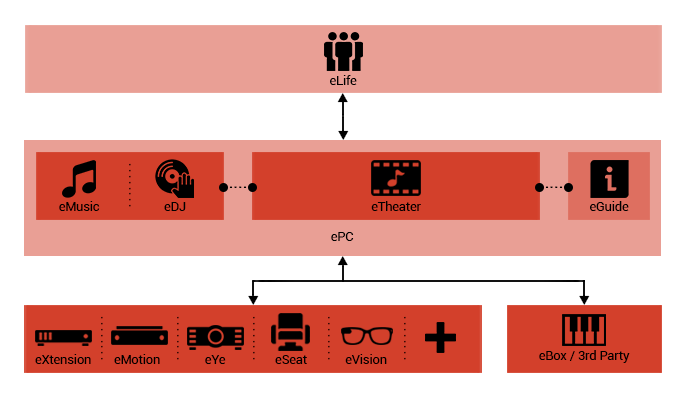
ePC
This unit acts as a powerful personal computer and due to
its diverse range of peripheral devices, provides users
with a wide range of options including but not limited to
TV receivers, home theatres, gaming consoles, smart homes,
and vehicle control.
The basis of the graphic environment
and GUI of this system is designed for the movement of the
human body, arms and hands. Therefore, the recognition part
of the system conducts a 3D scan of the user’s body and
issues movement commands. As a result, the user does not
need input devices such as a mouse or keyboard. An ePC gaming
console, entertainment, and home theatre system can provide
users with interesting options such as 3D hologram display,
running PC based games, light, sound control, and virtual
DJ.
eVision and eSeat are smart tools with the ability
to expand with the source code scripting. These smart tools
are able to add vision, touch and hearing abilities to the
multi-faceted and limitless boundaries of this system. Furthermore,
by using eBox cards, electronics, computer companies and
professionals are able to develop new advancements for this
system with relative ease. Various system tools and sensors
make it possible to monitor and report the user’s health,
nutritional needs, and physical movements.
This system
also stands out due to its ability to control and supervise
the user’s home and vehicle. This system is capable of controlling
home sub-systems, home appliances, and vehicles by connecting
to the Eternet Building and Eternet Vehicle services. These
features and capabilities are discussed in more detail in
the Eternet Building and Eternet Vehicle sections.
Hardware Specifications:
■ CPU: PC Based multi-core
■ Memory: Multichannel DDR RAM
■ GPU: AMD/NVIDIA/Intel
■ Connectivity/Expansion: eXtension Dock via USB 3.1/Thunderbolt,
eBox
■ Network: eWN, ePN, Wi-Gig via eXtension, Wi-Fi,
Bluetooth and Ethernet
■ A/V Tuner: DVB-S2/T2
■ A/V
Interface: Wired/Wireless HDMI, VGA
■ Storage: HDD, SSD
■ Optical Drive: Blue ray
Controllers & Interfaces:
■ eYe (3D Holographic projector/Display)
■ eMotion (3D
Motion sensor)
■ eVision (Smart Glasses)
■ eXtension
(Extension and charger dock)
■ eSeat (Smart massager,
entertainment and gaming seat)
■ eWatch (Smart watch
and biologic tracker)
■ eCho (Home theater speaker system)
■ eRein (Universal remote control)
■ eBoard (Multimedia
and gaming keyboard)
■ ePad (Game pad)
Service/Software:
■ OS: Linux/OS X/Windows family (A-Z sorted)
■ Speech
and Capture Motion: eMotion, eVision and eSeat controllers
■ Life: eLife, eGuide, eHealth, eNeighbor
■ Intelligent
Building/Vehicle: eControl, eGuide, eLife
■ Entertainment:
eGame, eTheater, eMusic, eDJ, eSense
■ Communication:
eNeighbor

-
Controlers
- echo
- emotion
- eseat
- evision
- ewatch
- extension
- eye
-
Networks and Services
- ebox
- econtrol
- egame
- eguide
- ehealth
- elife
- eneighbor
- etheater
- ewn
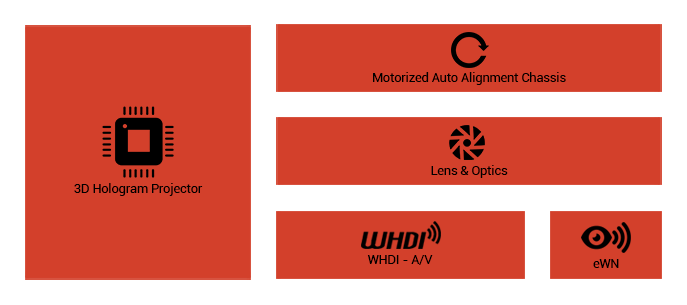
eYe
Different displays being supported by ePC provides a
platform for users to utilize several video outputs
regarding their needs. In addition, the physical dimensions
of the display screen plays a vital role in the utilization
of ePC services. Projectors are highly recommended choices
due to their affordability, large size, and the limitations
of TV displays.
This projector is able to display
3D and hologram images as a result of its versatile
and movable lens and chassis. Therefore, users can control
ePC images with their hands and fingers movement. Furthermore,
its embedded Wireless HDMI module can receive ePC images
remotely. This unit is also able to calculate depth
and direction via the available sensors and moves the
projector by means of the provided motors on the chassis
and lens. Exact placement of the image is also recognizable
and configurable by this system.
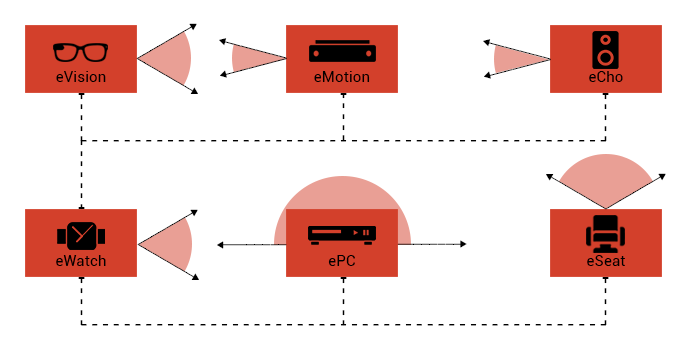
eCho
The gaming and multimedia unit of ePC supports different
audio outputs. The Surround 5.1 speaker system is introduced
for this purpose. eCho makes it possible to control
each speaker output by placing it on the eVision sightline.
Hence, users are able to control the volume and the
source of sound signal on each speaker, or set their
own voice (via eVision integrated microphone) as an
input source of any output channels. It should be mentioned
that eCho is able to simultaneously guide 5 channels
or sources to each of the outputs.
eMotion
eMotion is an image and motion processing system, able
to recognize horizontal movements of the body and vertical
motion of hands through vision and scanning capabilities.
The data is sent to a software engine in order to provide
more diverse and complex commands, in addition to just
movement of the hands and fingers. Two eMotion units
work simultaneously, one placed in front of the user,
aligned with the horizon to process body and hand movements
and the other, which is placed over the users head in
order to process hand and finger movement. It should
be mentioned that eMotion is also able to process movement
in both horizontal and vertical images, in solo mode.
By combining two eMotions at the same time, this system
provides us with 3D scan capabilities with enhanced
accuracy and an extended number of commands. The provided
engine in this system makes it able to track users and
the source of the motion, in order to maintain constant
visibility.
This controller enables its users to
execute their commands from a distance, without the
requirement of any input devices. This can be achieved
through their body and hands movement. eMotion analyzes
these movements and the user can issue gaming commands,
design, write, and control multi-media environments
including ePC.
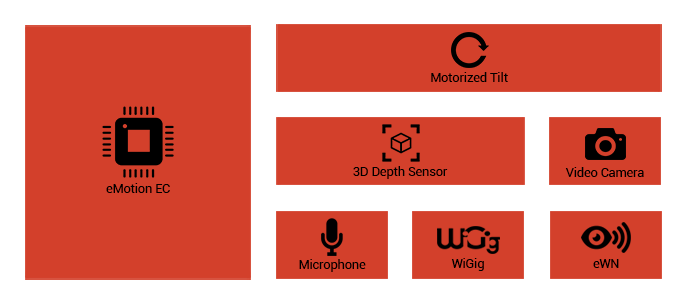
eSeat
eSeat is a smart electromechanical chair with full hardware
and software expansion capabilities. eSeat can be sub-categorized
as input and output due to its functionality.
■ Inputs:
Input units of eMotion module can vertically scan hands
and fingers, and also receive voice. Load cell and fingerprint
sensors are used for weight measurement and user recognition.
In addition, keyboard, driving, and flight control act
as interfaces between ePC and user.
■ Outputs: Embedded
jacks underneath this chair are responsible for all
movements, shaking, and vibrations in the chassis. Moreover,
motors and heaters can transfer movement, heat, and
vibrations to the user’s body. The provided speakers
on the chair make it possible to experience surround
sound.
As an interface between the user and ePC,
eSeat controls the ePC by receiving motion, sound, and
command information. ePC receives data and commands
from different hardware and software sources and uses
the power eSeat interface to provide movement, shaking,
vibration, and sound to the users.
eSeat provides
a touch, hearing, and sight interface between the user
and the ePC. These capabilities and services are provided
by eSense.
eSense is a software engine that receives
input data such as the user’s direction of sight (by
utilizing eVision), load cell and fingerprint sensor,
voice commands, hands movement, keyboard, and driving
and flight controllers in order to issue relevant commands
to ePC. On the other hand, it receives voice, motions
and relevant data from the ePC, and issues suitable
commands to controllers, motors, actuators, and speakers,
placed on the eSeat. This software engine is in charge
of the synchronization of motors and generates shaking
and harmonic motions based on the music rhythm and volume.
As a result, users can manage and control the music
or images with the motion and movement transferred to
the body. Furthermore, eSense provides the possibility
of pre-programmed or custom designed massages.
While
users utilize eWatch, eSeat can record vital signals
such as heart rate in different programs and functioning
modes. We can refer to this feature as another function
of eHealth. In addition, the eMotion module on the handle
of this chair, which is used to scan the user’s fingers
and hands, provides the exact designs and graphics.
eSeat can be connected to an ePC through eXtension via
Wi-Gig.
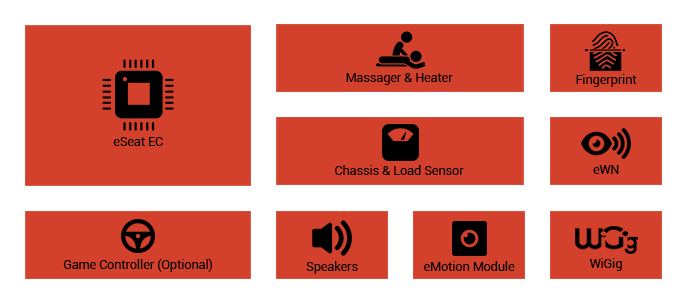
eVision
eVision was designed as a result of the importance of
smart glasses for Eternet. This controller is a wearable
computer which accommodates different services of Eternet
Computer, Eternet Building, and Eternet Vehicle. Photography,
browsing, speech translation, listening to music, making
and answering calls, watching 3D images and controlling
electronic devices are some of the capabilities of eVision.
Moreover, eVision enables users to control GUI environments
by their hand and fingers movements via 3D Depth Sensor.
They can also issue voice commands to benefit the available
abilities of this smart glass.
Supervision and control
of tools and devices of Eternet is another capability
of eVision. By using eWN, eVision can directly communicate
with different nodes via service providers. As a result,
it informs the users about the availability of nodes
after considering different scenarios, access patterns,
field of sight, and functionality. This enables the
user to control or manage them. Services provided by
this gadget are quite diverse.
A concise list of
the common and default services of eVision and other
Eternet servers is provided below:
■ eControl: allows
the user to access, manage, and control nodes, such
as service providers, controllers, and home appliances.
■ eGuide: is a suggestion and warning providing
system, and is in charge of announcing the availability
of any nodes in the field of visibility.
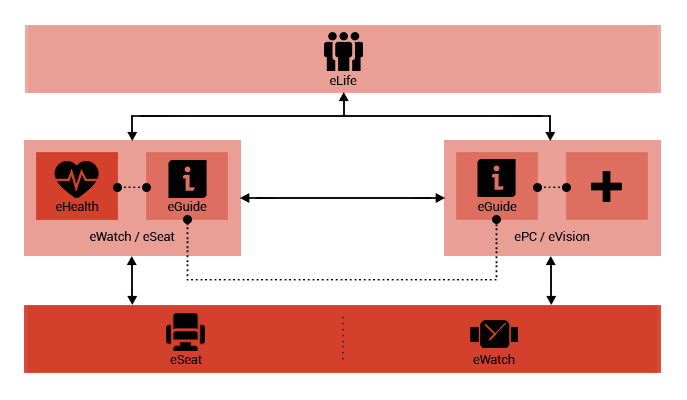
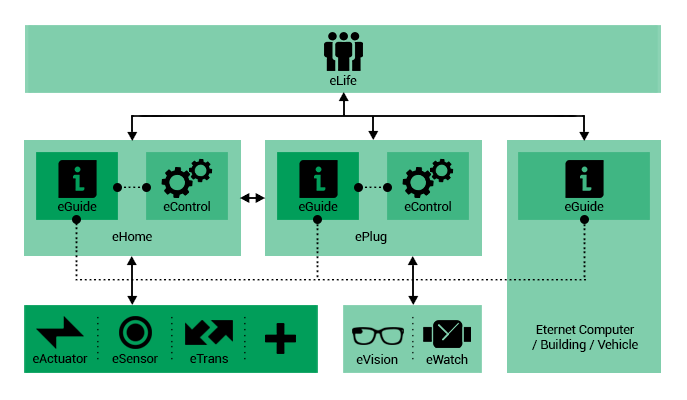
■ eLife:
provides an online platform for accessing services that
facilitate communication between Eternet sub-systems.
■ eMusic: is a software service used to search for
and play music. It also provides a social network for
music related activities.
■ eNeighbor: manages and
controls connections between people, buildings, and
vehicles, based on their physical locations.
As
it was mentioned earlier, there are many possibilities
to expand eVision services. For example, eGuide enables
users to receive subtitles in different languages. Moreover,
this system makes it possible to receive navigation
information while driving. It should be noted that eVision
can be connected to an external battery in order to
increase its operation time span.
eWatch
This device is considered a smart watch which manages
calls and messages and also receives the user’s vital
signs, such as the heart rate. eWatch also acts as a
cell phone which works along e-Vision to make Heads
Up Display calls possible. In order to perform
this function, eWatch connects the users to the GSM
Network, and eVision acts as a Headset.
Similar to
eVision, eWatch also supports a variety of different
software services. Services such as eControl, eGuide
and eNeighbor, allow the user to control, supervision
and make calls with their smart watch, respectively,
as well as other features, capabilities, and services.
Kinetic charging allows users to keep this device charged,
using the motion of their wrist. This eliminates the
need to plug it into a charger, periodically.
One
of the main goals in designing eWatch is to provide
constant supervision of the user’s health and well being.
By using eHealth and eLife services, the eWatch designated
sensors provide the users with information regarding
physical activity, sleep, and nutrition. Based
on this set of information, this system also makes useful
suggestions to the users for maintaining and improving
their well being.
eWatch uses sophisticated sensors
to determine the user’s heart rate, blood oxygen level,
as well as the frequency of radio waves in their environment.
In order to display a more comprehensive picture of
the user’s health and well being, eWatch compares this
collected information and parameters to the user’s physical
activity. By using NFC and fingerprint, eWatch
also provides useful tools for electronic payment and
ID verification.
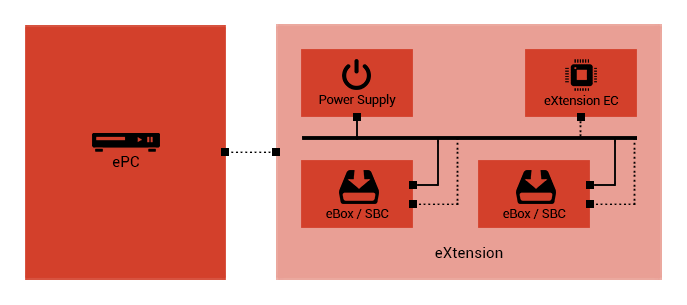
eXtension
The main purpose of eXtension is to expand the ePC’s
hardware capabilities. This allows computer companies
to design affordable eBoxes, providing users with a
wide variety of products with differing specifications
and capabilities. Ventilated, cooled, and self-power
supplied eBox magazines are desirable platforms for
different electronic and computer products.
Equipping
eXtension with Wi-Gig module enables eMotion and eSeat
to be connected wirelessly. Therefore, eXtension is
known as the fastest wired and wireless gateway of Eternet
Computer for interacting with different devices and
systems.
eXtension is also a wireless charging and
connection hub for peripheral devices such as ePad,
eBoard and eRein. In addition, it provides a variety
of connection solutions for other devices such as USB
series, Thunderbolt, eSATA, HDMI, and DMX. The available
DMX port on eXtension makes it possible to connect lighting
and stage effects devices to the ePC.
eDJ is another
one of the capabilities included in this system. This
software uses eMotion movement recognition tool and
communicates through DMX with lighting and stage effects
devices. Hence it can control and alter programmed images
on music tracks. So, users can generate those images
using the movement of their body and hands, by means
of eMotion and eBoard.
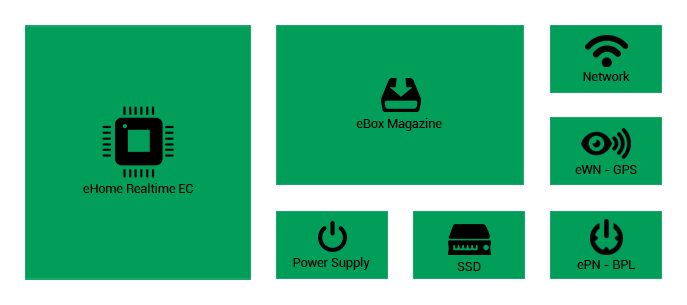
eBox
eBox is a platform for introducing new hardware parts
to ePC and eHome. The eBox platform makes it possible
for electronic and computer manufacturers to expand
the hardware capabilities of their products with Eternet
features. This platform uses an ePort to provide required
power and computer connection. Therefore, an ePort contains
USB/Thunderbolt interfaces and 5/12 volt power ports.
It should be mentioned that devices using eBox as an
expansion platform which operates with eHome, need to
be designed based on Single-Board Computer (SBC) architecture.
This will ensure the performance and stability of eHome
as a real-time server.
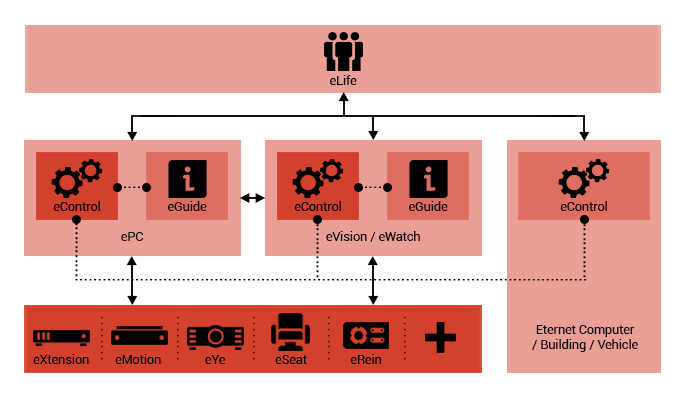
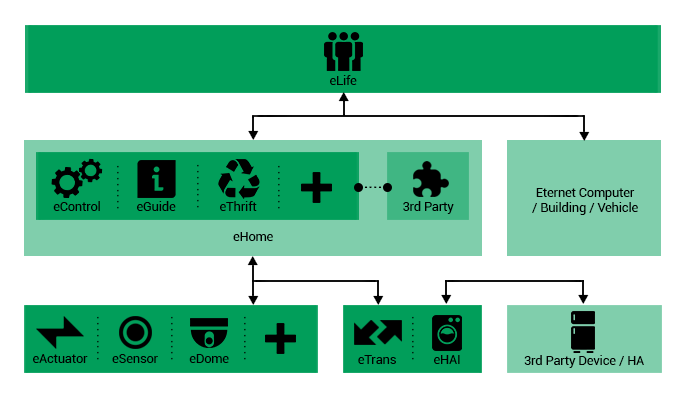
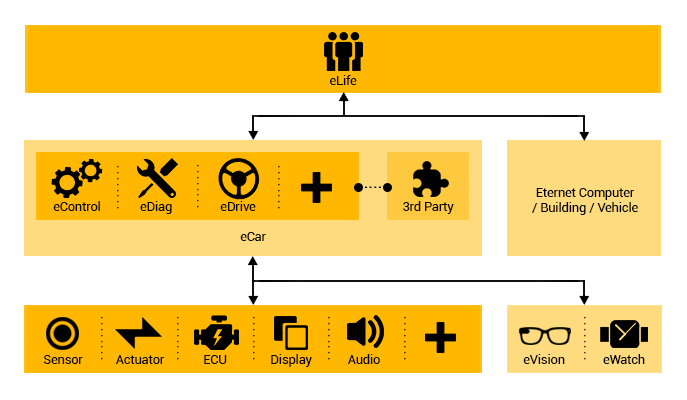
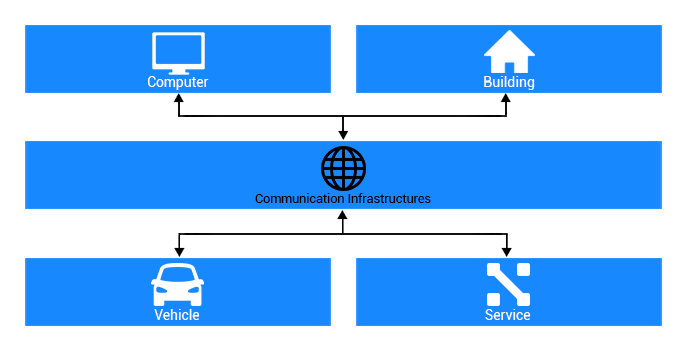
eControl
An Eternet Computer package consists of a personal computer,
peripheral devices, and a connection to the Eternet
Service network, which provides a range of artificial
intelligence based services and abilities for users
with different levels of computer knowledge, and different
electronic devices. The user’s senses/behavior is used
to control the system’s behavior in different conditions
and scenarios. Therefore, some services are designed
in order to control and enhance the user’s health and
lifestyle.
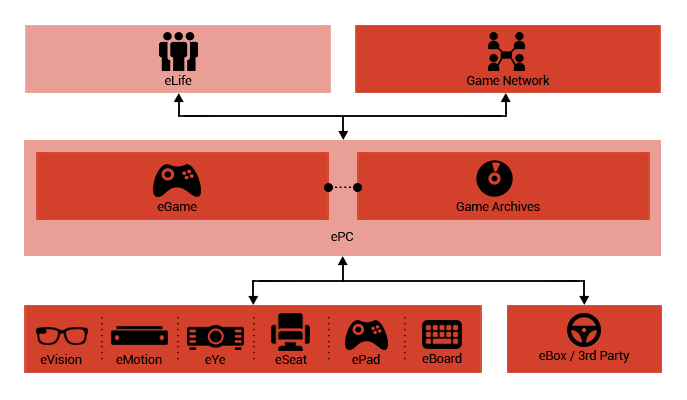
eGame
Video games are a significant contributor to computer
system sales. Therefore, gaming holds a special place
in this system. An eGame with a proper hardware and
software architecture, and controlling devices like
eMotion, eVision, eSeat, eBoard and ePad provides a
desirable environment for running different types of
computer games where some of these abilities are not
available in conventional consoles. eVision, another
feature of such consoles, is used for internal communication
in order to provide text, voice and video communication.
eSeat is a tool to transfer senses such as movement
and vibration to the gamer or control a vehicle or aircraft
using arm and hand movements.
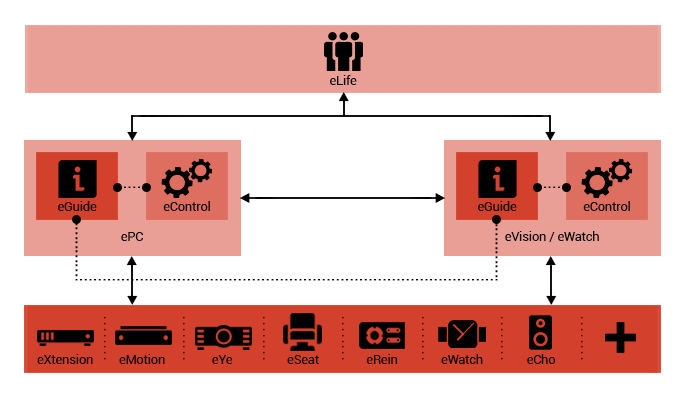
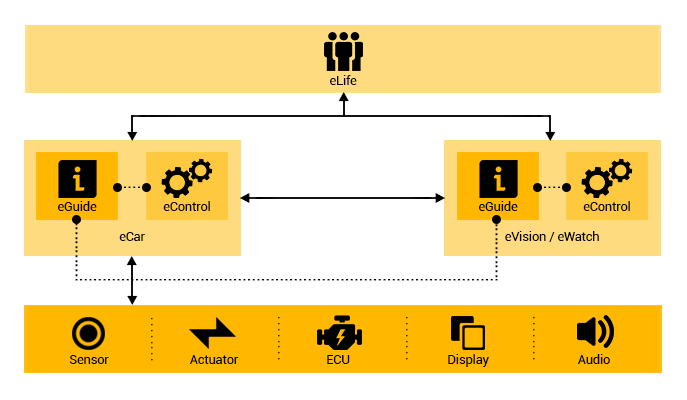
eGuide
eGuide is a software service, available on ePC server
and eVision controller. As a communication medium, receives
the data from eLife servers and displays information
to users via ePC and eVision. eGuide informs the users
on the existence of any electronic and computer devices
visible to eVision. This is possible by means of eWN.
Moreover, users can monitor and control the parameters
of such devices. It should be mentioned that offline
and local configuration of any section of an Eternet
is possible via eGuide.
eHealth
Providing and maintaining the user’s health and comfort
is one of the most advanced goals in the design of an
Eternet. eHealth service receives biological information
of the users through eWatch, and eSeat and monitors
their health, movement, and nutrition. By analyzing
this information, this service provides users with a
variety of suggestions, notices, and warnings regarding
their health and well-being.
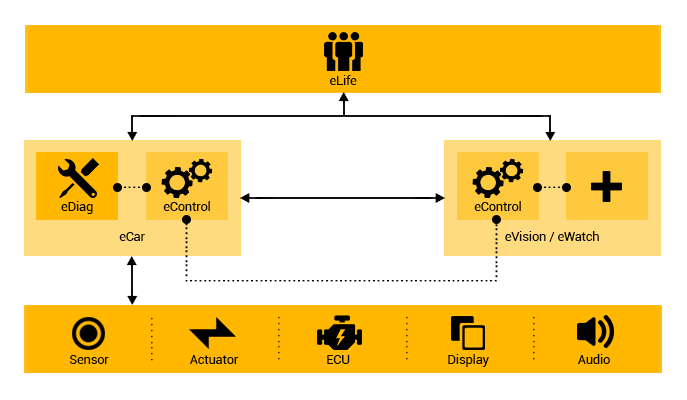
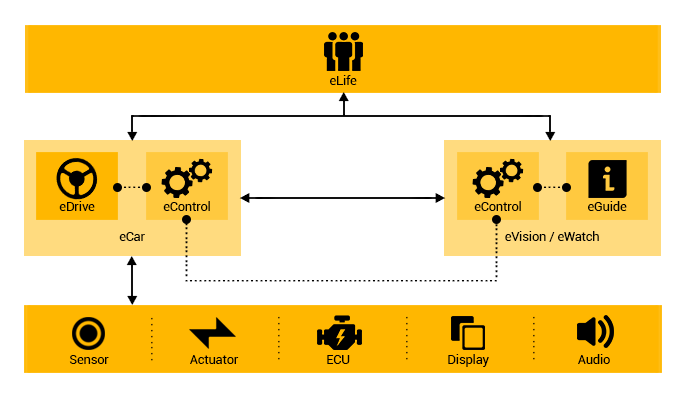
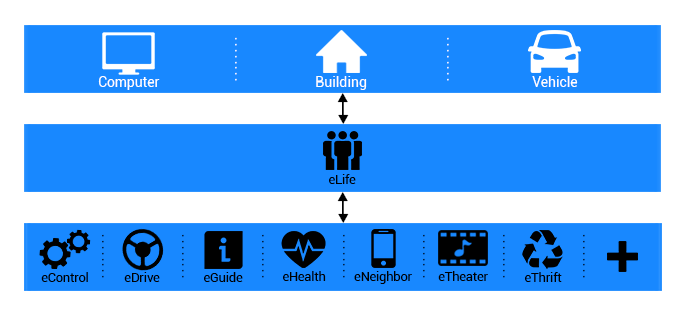
eLife
eLife is an Eternet Service sub-system and one of its
cloud services. It provides a platform for the execution
and management of software systems such as eGuide, eControl,
eHealth and eNeighbor. eLife gathers information about
the user’s family, job, behavior, routines, interests,
and other life characteristics by using tools such as
eWatch, eVision, and social networks. Therefore, it
can provide suggestions or warnings via eGuide based
on the life styles of different users or other relevant
Eternet systems and controllers. In addition, eLife
makes it possible to access other devices or systems
that have been placed in different geographical locations
on the Eternet network.
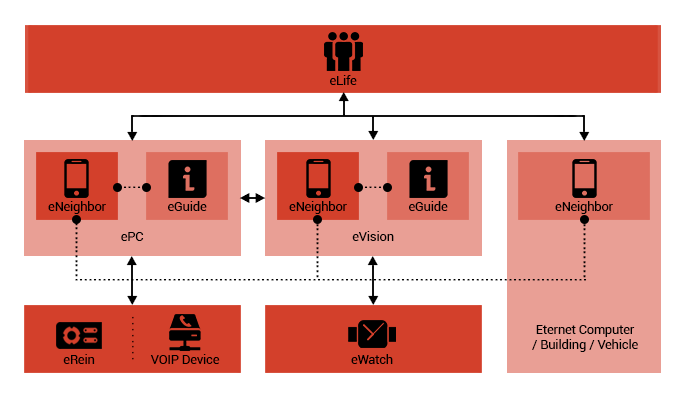
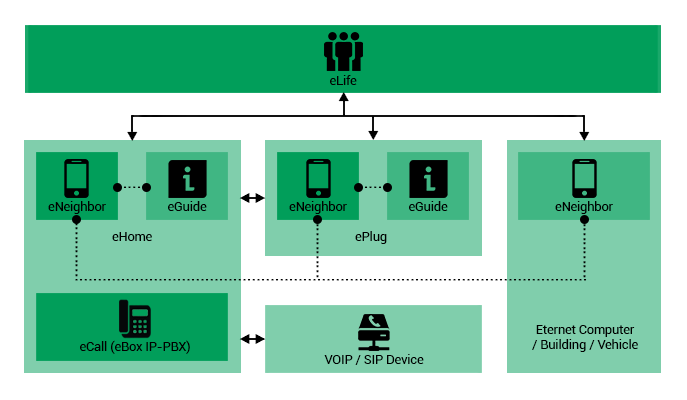
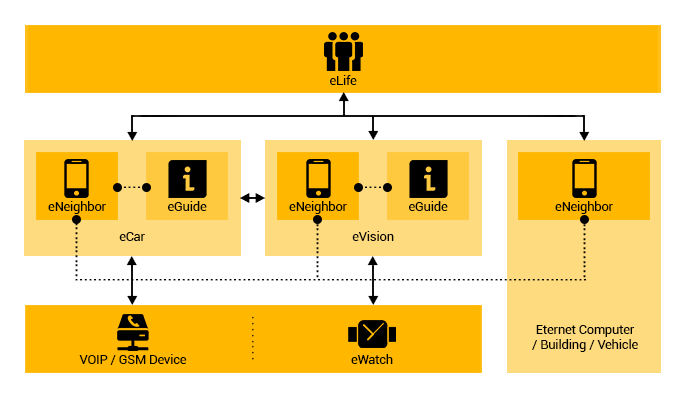
eNeighbor
Is a software service, enables users to be connected
to friends as well as people on their contact lists.
Incoming and outgoing calls management is also a defined
task for eNeighbor. The contact list provides the Eternet
IDs of people, buildings, or vehicles. eNeighbor makes
it possible to search for people, buildings, and vehicles,
placed at different physical locations based on their
physical, social, personal data, and privacy settings.
Moreover, users can track family members and vehicles.
This feature is especially useful for providing support
and comfort to parents interested in monitoring child
safety.
eTheater
As it was mentioned earlier, ePC is designed on the
Home Theater PC platform which provides unique home
theater features for users, based on the available controlling
devices. Watching photos, movies, optical discs, and
Internet TV on different televisions and projectors
is one of the advanced features provided by Wireless
HDMI. Additionally, such devices can be controlled using
motion sensing techniques which makes the users able
to remotely control their devices by arms and body movements.
Equipping this system with cable receivers and digital
satellite (DVB-S2/T2) provides the capability of easy
television and radio channels reception, and recording.
This system also supports HD and 3D channels reception
while utilization of eVision allows users to choose
their preferred language or subtitles.
In addition,
the use of eVision as 3D active glasses makes it possible
for users to watch 3D images on a TV display and to
personalize their audio and subtitles. Hence, each user
can receive a different set of audio or subtitles on
the same video.
eTheater provides special services
for music enthusiasts as explained below:
■ eMusic:
A software service for accessing, searching, receiving
and playing music. In addition, it is a social network
service provider which can be utilized to find users
with the same taste of music (This service is explained
in detail in the Eternet Service section).
■ eDJ:
This software is considered a Computer DJ. By employing
this software, users can convert their body, hands and
fingers movements to music visualization by means of
eMotion and eBoard. As a result, motion pictures, synchronized
with the music and body movements can be produced using
proper codes and equations. eDJ also supports lighting
and stage effects devices based on the DMX standard
via eXtension controller.
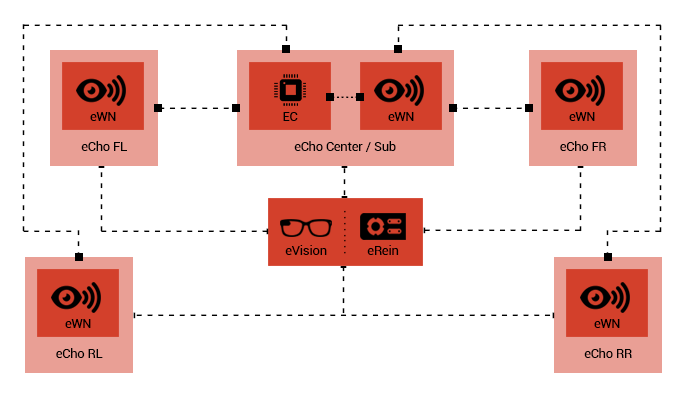
eWN
eWN is a group of nodes, communicating via Bluetooth
Smart, based on the information provided by Accelerometer-Gyro-Compass
sensors. eWN can perform its task of connecting two
nodes in two different modes:
■ 2D: Based on the
services being provided by nodes, they evaluate some
parameters to find their 2D Direction and 2D viewing
angles relative to others nodes. After considering the
priority feature indicated by signal strength parameter,
they perform data and service sharing.
■ 3D: In order
to communicate via Bluetooth Smart, nodes receive data
about the angle of sight in relation to the horizontal
and vertical axis (3D direction indicator) and viewing
cone (3D viewing cone). Whenever these features overlap,
the nodes start to communicate and provide services,
according to defined scenarios, using the signal strength
parameter.
Nodes can change communication priorities
or disconnect it by evaluating scenarios, preferences,
and parameters in eWN mode. Moreover, eWN enables computer,
electronic devices, and systems to provide augmented
reality and visual reciprocity.